Fresh, Frozen, and Canned Vegetables
 Vegetables are the cornerstone of a healthy diet, offering a plethora of essential nutrients that support optimal health. From vitamins and minerals to fiber and antioxidants, these plant-based foods provide a wide range of benefits. Regardless of whether they are fresh, frozen, or canned, vegetables remain nutritional powerhouses.
Vegetables are the cornerstone of a healthy diet, offering a plethora of essential nutrients that support optimal health. From vitamins and minerals to fiber and antioxidants, these plant-based foods provide a wide range of benefits. Regardless of whether they are fresh, frozen, or canned, vegetables remain nutritional powerhouses.
Fresh Vegetables
Fresh vegetables are generally considered the most nutritious option, as they are often consumed soon after harvest, minimizing nutrient loss. They offer a wide variety of textures, flavors, and colors, making them appealing and versatile in meal preparation. However, fresh vegetables can be perishable, requiring proper storage and timely consumption to prevent spoilage.
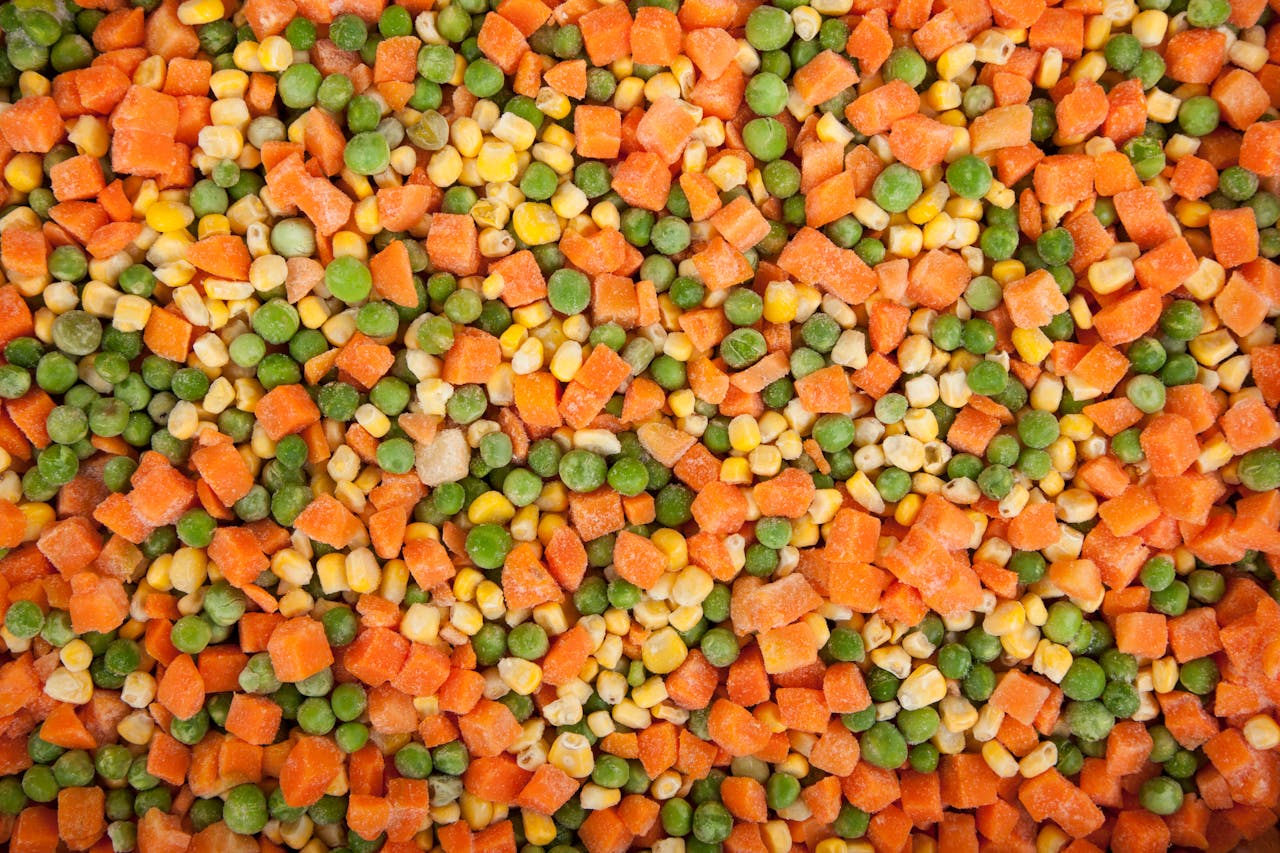
Frozen Vegetables
Frozen vegetables are a convenient and nutritious alternative to fresh produce. They are often flash-frozen immediately after harvest, preserving their nutrients and preventing spoilage. Frozen vegetables can be a great option for individuals with busy lifestyles or limited access to fresh produce. Be mindful of the potential for added ingredients – they may contain a slightly higher sodium content due to added preservatives, but they are still a healthy choice.
In addition to the sodium content, another concern with frozen vegetables is the potential for added fatty, salty, or sugary sauces. Many frozen vegetable mixes come pre-seasoned with sauces that can significantly increase calorie, fat, and sodium content. I recommend carefully checking the nutrition label, opting for products without added sauces, and using your own healthy seasonings like herbs, spices, or lemon juice.
Canned Vegetables
Canned vegetables are another convenient option, offering a long shelf life and easy preparation. They are often processed at high temperatures, which can lead to some nutrient loss, but canned vegetables are still a good source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. To maximize nutritional value and minimize added unhealthy components, look for products labeled “no salt added” or at a minimum “low sodium.” I also encourage you to check for the absence of added sugars and unhealthy fats, and consider rinsing canned vegetables thoroughly with cold water to remove excess sodium and preservatives.
Closing Thoughts
I’m often asked which is the best choice – ultimately, the best choice is the one that you will consistently incorporate into your diet, and may depend on factors such as convenience, cost, and personal preference. For example, if you find fresh vegetables challenging to prepare or store, frozen or canned options can be excellent substitutes. The key is to choose vegetables that you enjoy and that fit your lifestyle. Vegetables are essential for a healthy diet, regardless of whether they are fresh, frozen, or canned.
Matthew A. Webster, MA, MS, ED.D, LPC
Dr. Matt Webster is a professional educator, nutritionist, and therapist located in the Houston, Texas area. He specializes in couples therapy, sexuality, and maladaptive eating patterns with a focus on the role of nutrition. More About Matt >>
Last modified:









